least count of brinell hardness tester|brinell hardness testing machine diagram : purchasers The Brinell Hardness Test method is the most commonly used hardness measurement technique in the industry. In the Brinell Hardness Testing, the hardness of a metal is determined by measuring the permanent indentation size produced by an indenter.
Choose Thermo Scientific™ Nalgene™ Autoclavable Carboys for large batches of culture media, vaccine product production, bulk media and chemical storage. These carboys feature a large mouth for easy filling/dispensing, and are .
{plog:ftitle_list}
In healthcare, ensuring the sterility of medical instruments is crucial. Steam sterilization, or autoclaving, stands as a key defense against microbial contamination. Utilizing steam under pressure, this method .
The Brinell Hardness Test method is the most commonly used hardness measurement technique in the industry. In the Brinell Hardness Testing, the hardness of a metal is determined by measuring the permanent indentation size produced by an indenter. Harder materials will generate shallow indentations . See moreThe Brinell Hardness Test is performed in a Brinell Hardness Test Unit. In this test method, a predetermined force (F) is applied to a tungsten carbide ball of fixed diameter (D), held for . See moreOnce the average indentation diameter is measured the Brinell Hardness Number (BHN or HBW) can be calculated using the following Brinell hardness test formula: Here, 1. F=Applied force, in kgf 2. D=diameter of indenter, in mm 3. d=diameter of . See more
laboratory autoclave repair and service wa
The BHN or HB values are mostly reported using only the number. So, it seems there is no unit for the Brinell Hardness Number. . See moreBrinell testing of a material with different ball diameters and test forces must be conducted within the same force-diameter index ("Brinell test procedure") in order to enable direct comparison of the measured hardness values.The Brinell Hardness Test method is the most commonly used hardness measurement technique in the industry. In the Brinell Hardness Testing, the hardness of a metal is determined by measuring the permanent indentation size produced by an indenter.Brinell testing of a material with different ball diameters and test forces must be conducted within the same force-diameter index ("Brinell test procedure") in order to enable direct comparison of the measured hardness values.
The Brinell hardness test is a widely recognized method for determining the hardness of various materials. It involves applying a constant load or force, typically ranging from 187.5 to 3000Kgf, for a specified time period, usually between 10 and 30 seconds.
See Brinell Conversion Charts located in this operation manual. All Brinell Values should be reported with the load, ball size, ball material, and time-at-load if it is not the most common 3000kg, 10mm tungsten ball, and 10-15 seconds time-at load.The ASTM’s Brinell hardness test standard is used by alloy and metal suppliers and users, and it’s a basic requirement for all hardness testing equipment. This kind of hardness testing is used to measure the hardness and toughness of metallic materials.The five common force-diameter indexes are 1, 2.5, 5, 10 and 30. Testing of a material with different ball diameters and test forces must be conducted within the same force-diameter index in order to achieve comparable test results (see overview table "Brinell methods and applications”).
The general principle of the Brinell indentation hardness test consists of two steps: The indenter is brought into contact with the test specimen in a direction perpendicular to the surface, and the test force is applied (Apply the test force within 1 to 8 s).Test forces range from 500 to 3000 kgf. A Brinell hardness result measures the permanent width of indentation produced by a carbide indenter applied to a test specimen at a given load, for a given length of time. EN ISO 6506-1 is a European standard that specifies the requirements for metallic materials' Brinell hardness testing. It outlines the testing method, equipment, calibration, and procedures for determining the Brinell hardness of metallic materials using test forces between 1.96 N and 29420 N.A well structured Brinell hardness number reveals the test conditions, and looks like this, "75 HB 10/500/30" which means that a Brinell Hardness of 75 was obtained using a 10mm diameter hardened steel with a 500 kilogram load applied for a period of 30 seconds.
The Brinell Hardness Test method is the most commonly used hardness measurement technique in the industry. In the Brinell Hardness Testing, the hardness of a metal is determined by measuring the permanent indentation size produced by an indenter.
Brinell testing of a material with different ball diameters and test forces must be conducted within the same force-diameter index ("Brinell test procedure") in order to enable direct comparison of the measured hardness values.The Brinell hardness test is a widely recognized method for determining the hardness of various materials. It involves applying a constant load or force, typically ranging from 187.5 to 3000Kgf, for a specified time period, usually between 10 and 30 seconds.See Brinell Conversion Charts located in this operation manual. All Brinell Values should be reported with the load, ball size, ball material, and time-at-load if it is not the most common 3000kg, 10mm tungsten ball, and 10-15 seconds time-at load.
The ASTM’s Brinell hardness test standard is used by alloy and metal suppliers and users, and it’s a basic requirement for all hardness testing equipment. This kind of hardness testing is used to measure the hardness and toughness of metallic materials.
The five common force-diameter indexes are 1, 2.5, 5, 10 and 30. Testing of a material with different ball diameters and test forces must be conducted within the same force-diameter index in order to achieve comparable test results (see overview table "Brinell methods and applications”).The general principle of the Brinell indentation hardness test consists of two steps: The indenter is brought into contact with the test specimen in a direction perpendicular to the surface, and the test force is applied (Apply the test force within 1 to 8 s).
Test forces range from 500 to 3000 kgf. A Brinell hardness result measures the permanent width of indentation produced by a carbide indenter applied to a test specimen at a given load, for a given length of time. EN ISO 6506-1 is a European standard that specifies the requirements for metallic materials' Brinell hardness testing. It outlines the testing method, equipment, calibration, and procedures for determining the Brinell hardness of metallic materials using test forces between 1.96 N and 29420 N.
laboratory autoclave repair aservice
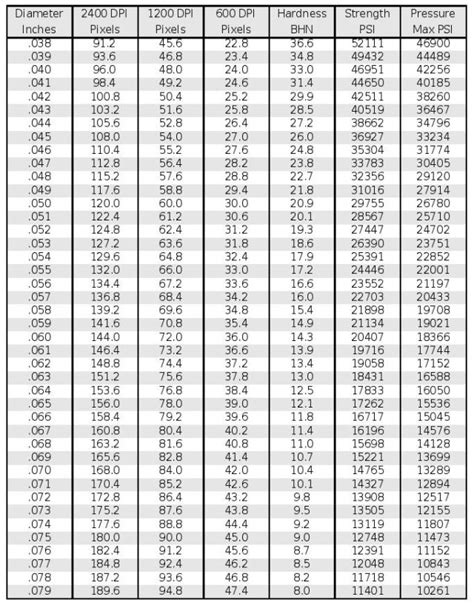
lee brinell hardness tester chart
laboratory autoclave repair service
brinell hardness testing machine diagram
brinell hardness testing charts
This manual is a general presentation of your product and it will give you important details to help you to solve possible problems. Please, read it and keep this with you.
least count of brinell hardness tester|brinell hardness testing machine diagram